MlaC belongs to a unique class of non-canonical substrate-binding proteins and follows a novel phospholipid-binding mechanism - ScienceDirect

Phospholipid Membrane Fluidity Alters Ligand Binding Activity of a G Protein-Coupled Receptor by Shifting the Conformational Equilibrium | Biochemistry
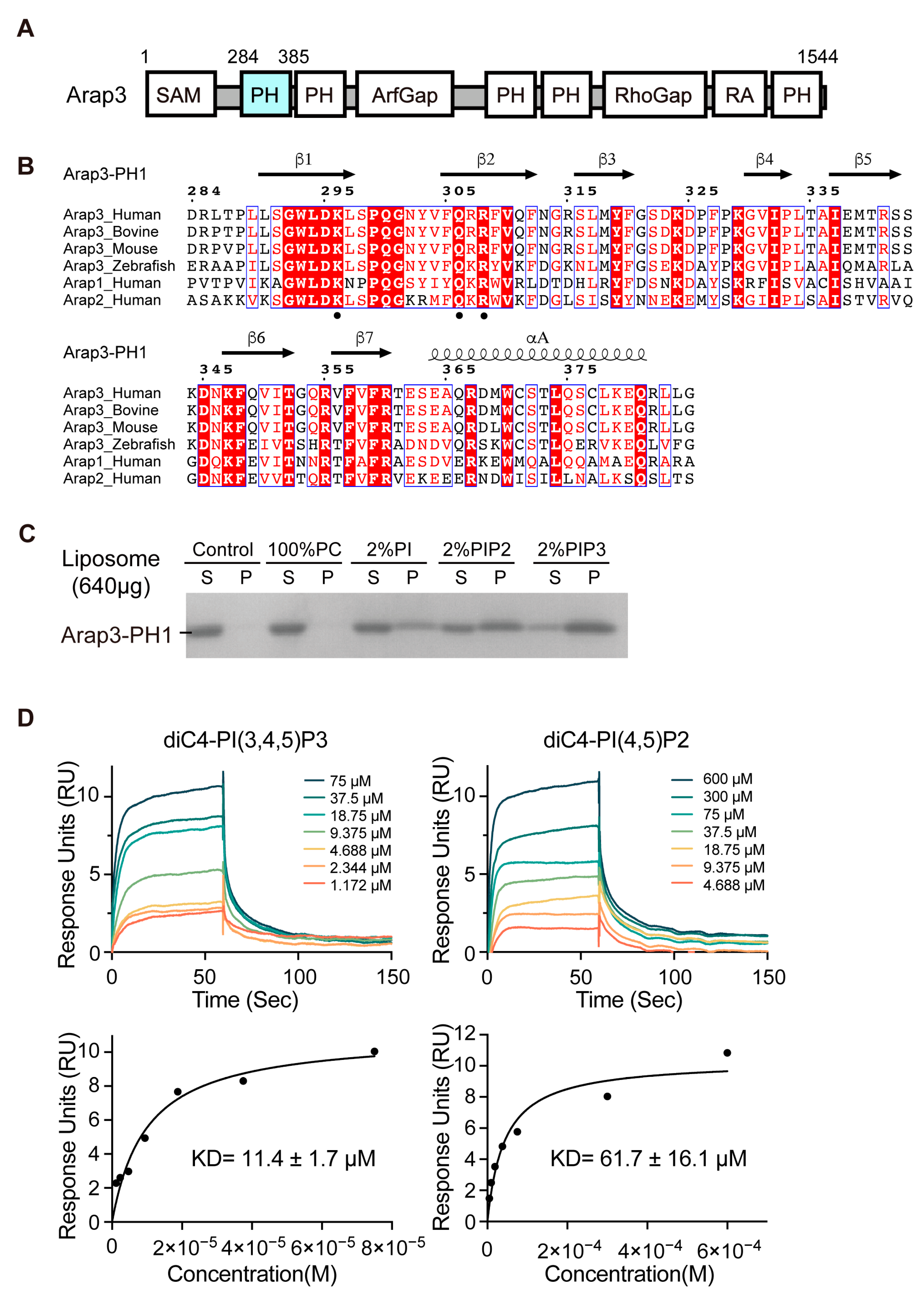
IJMS | Free Full-Text | Structural Insights Uncover the Specific Phosphoinositide Recognition by the PH1 Domain of Arap3
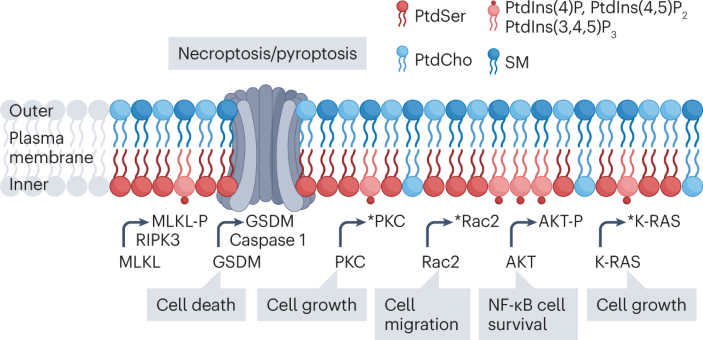
Regulation of phospholipid distribution in the lipid bilayer by flippases and scramblases | Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology

Phospholipid-binding proteins differ in their capacity to induce autoantibodies and murine systemic lupus erythematosus - JS Levine, R Subang, S Setty, J Cabrera, P Laplante, MJ Fritzler, J Rauch, 2014
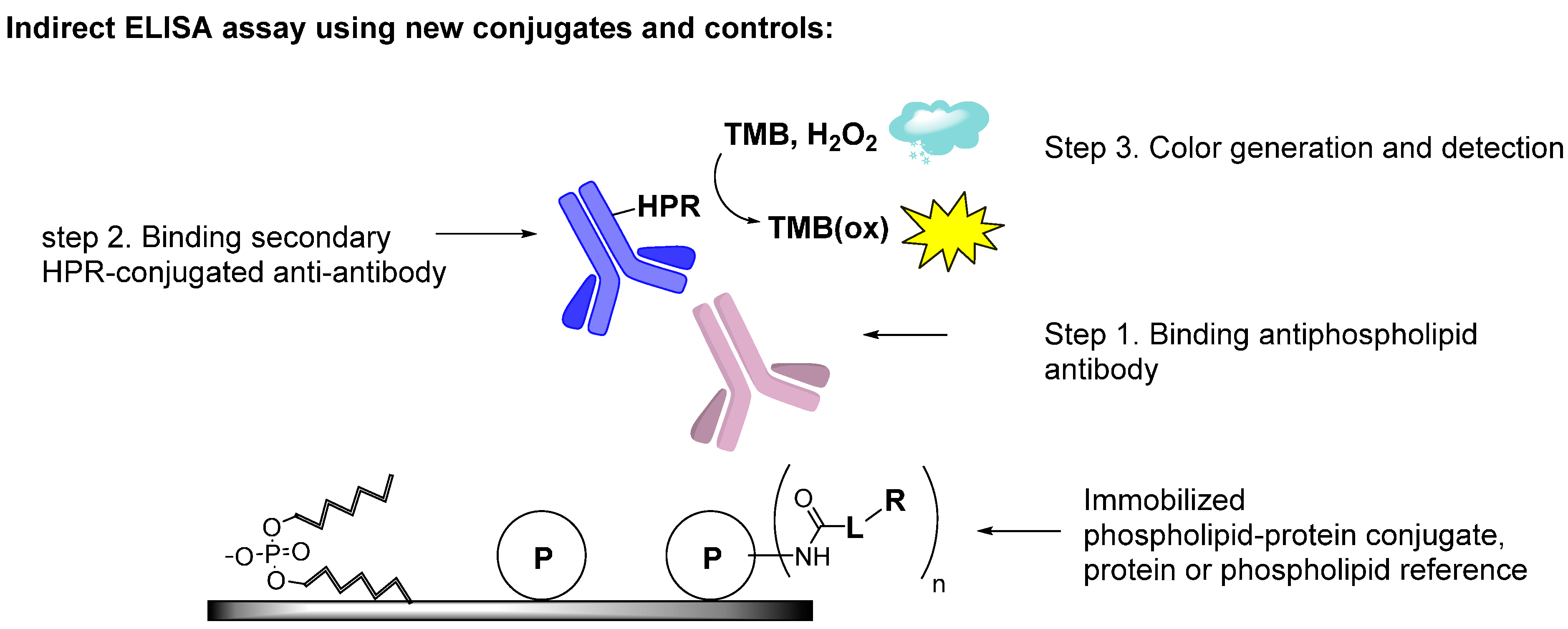
Molecules | Free Full-Text | Synthesis of Phospholipid-Protein Conjugates as New Antigens for Autoimmune Antibodies

A simple guide to biochemical approaches for analyzing protein–lipid interactions | Molecular Biology of the Cell

Coordination of Phospholipid-Based Signaling and Membrane Trafficking in Plant Immunity: Trends in Plant Science

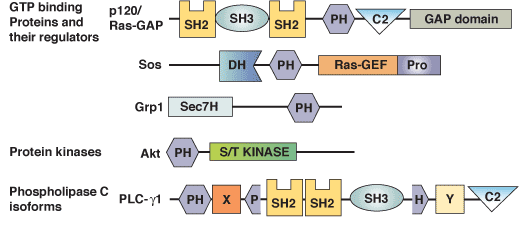
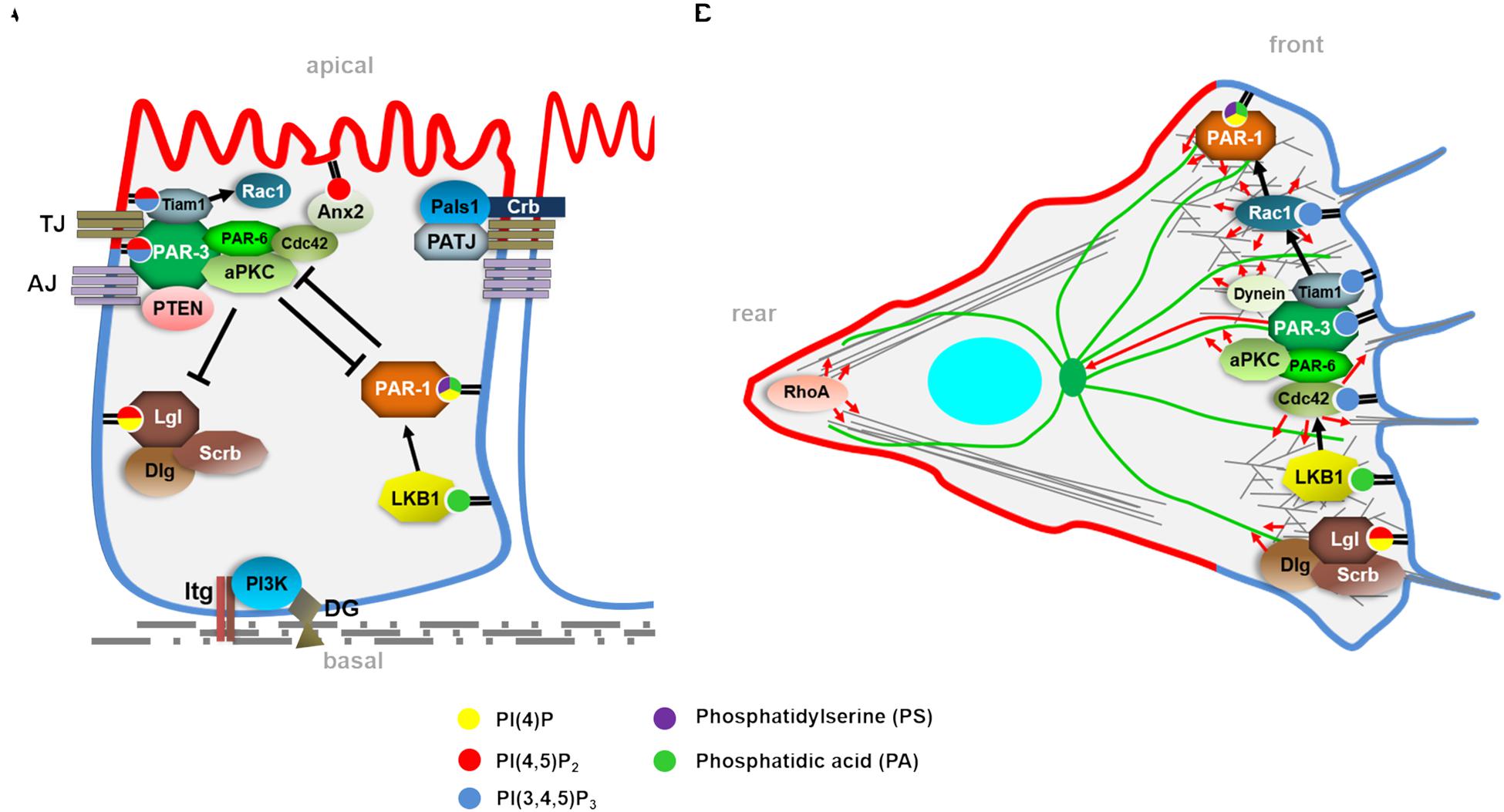
Kinase Associated-1 Domains Drive MARK/PAR1 Kinases to Membrane Targets by Binding Acidic Phospholipids: Cell

The phospholipid code: a key component of dying cell recognition, tumor progression and host–microbe interactions | Cell Death & Differentiation

Ligand–Phospholipid Conjugation: A Versatile Strategy for Developing Long-Acting Ligands That Bind to Membrane Proteins by Restricting the Subcellular Localization of the Ligand | Journal of Medicinal Chemistry

Phospholipid-Binding Protein EhC2A Mediates Calcium-Dependent Translocation of Transcription Factor URE3-BP to the Plasma Membrane of Entamoeba histolytica | Eukaryotic Cell
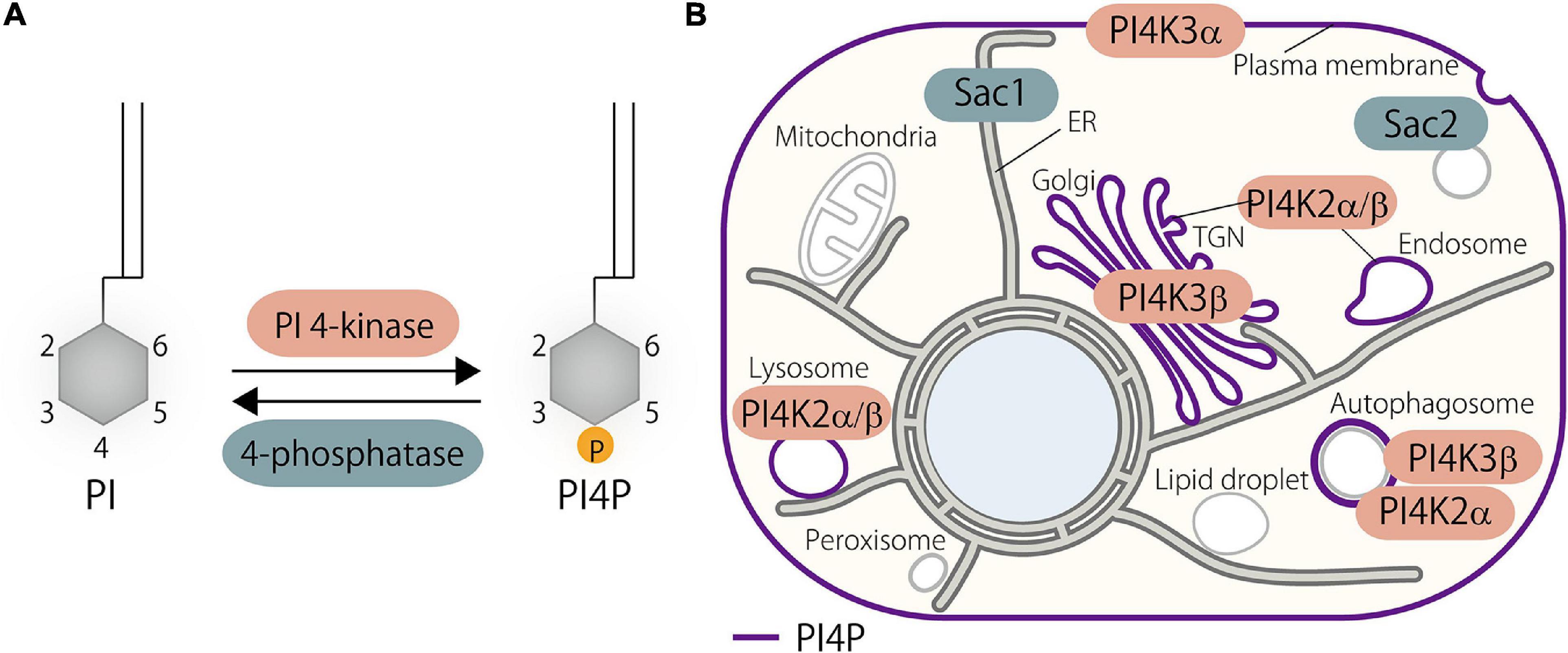
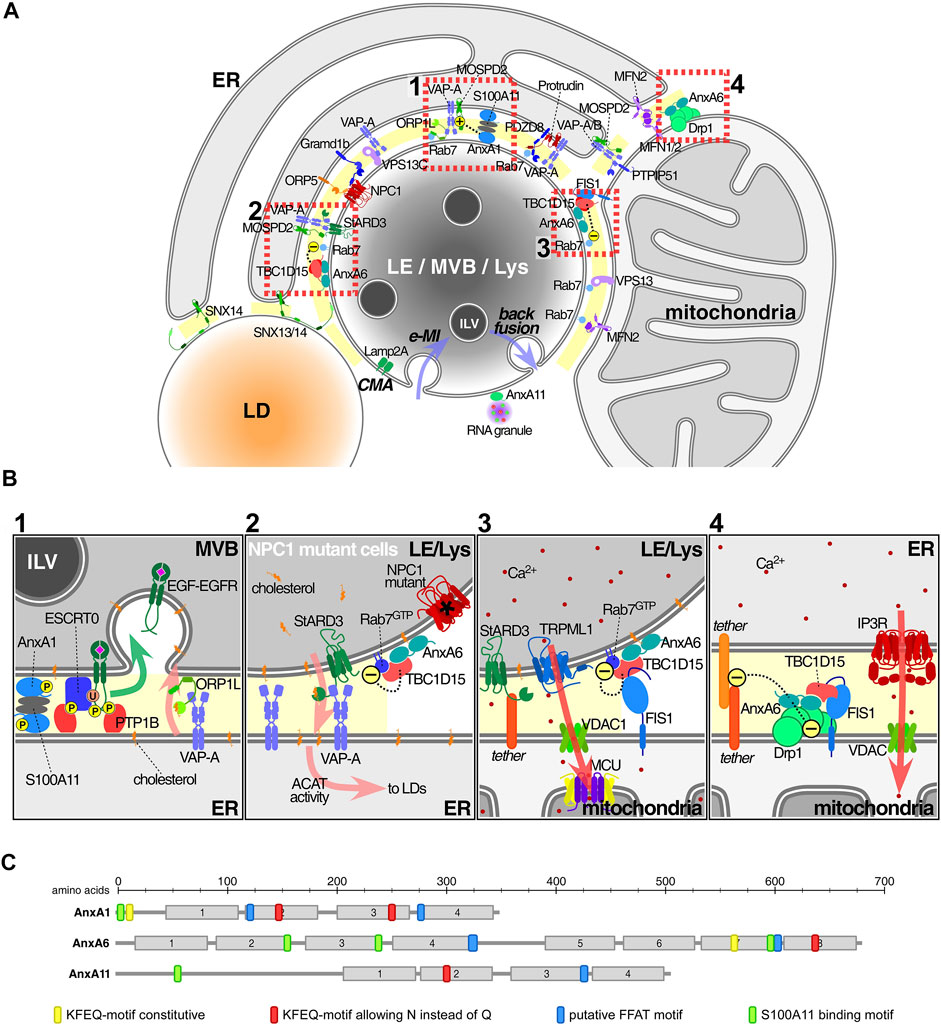
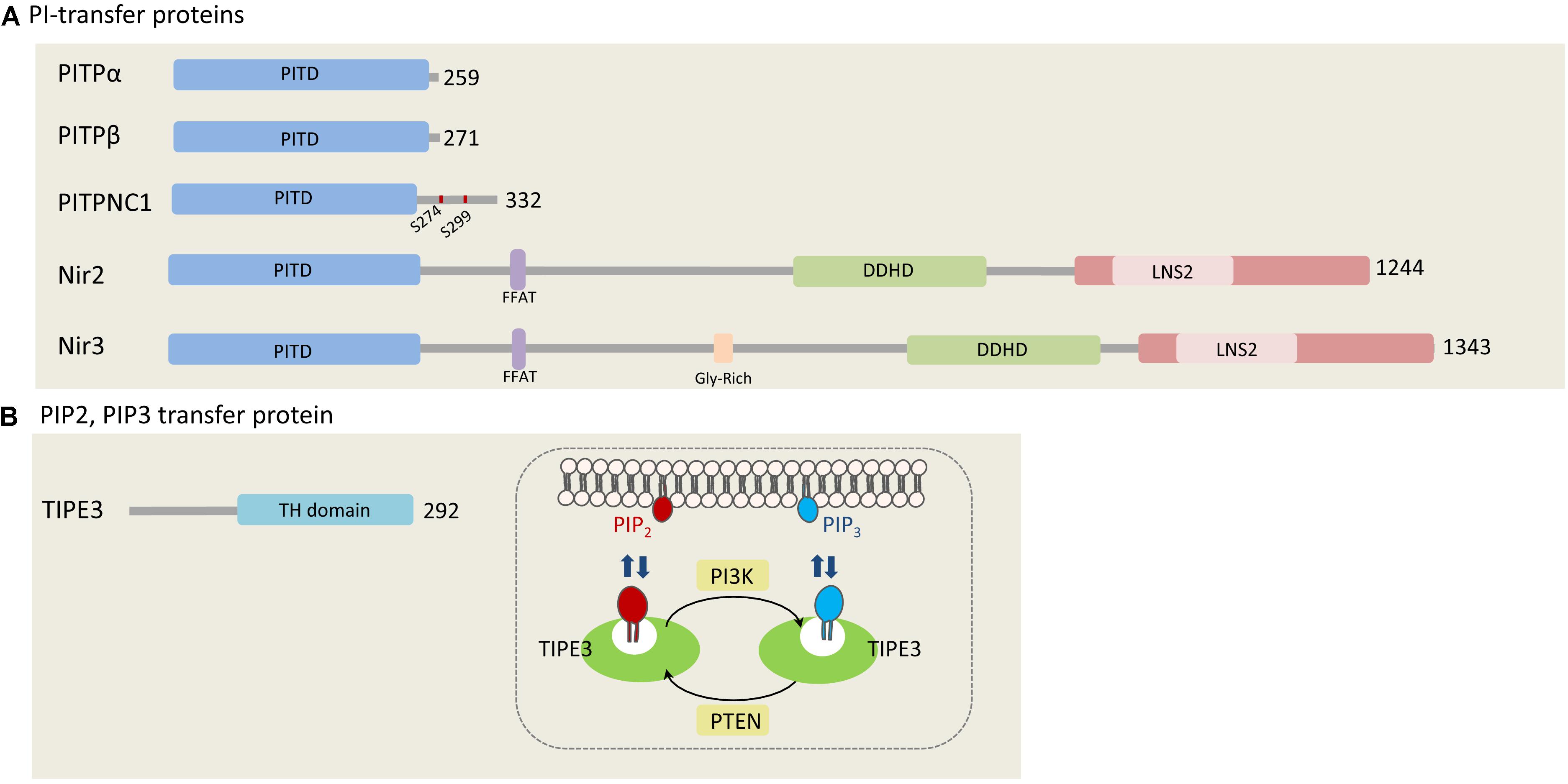
Frontiers | Functions of Oxysterol-Binding Proteins at Membrane Contact Sites and Their Control by Phosphoinositide Metabolism