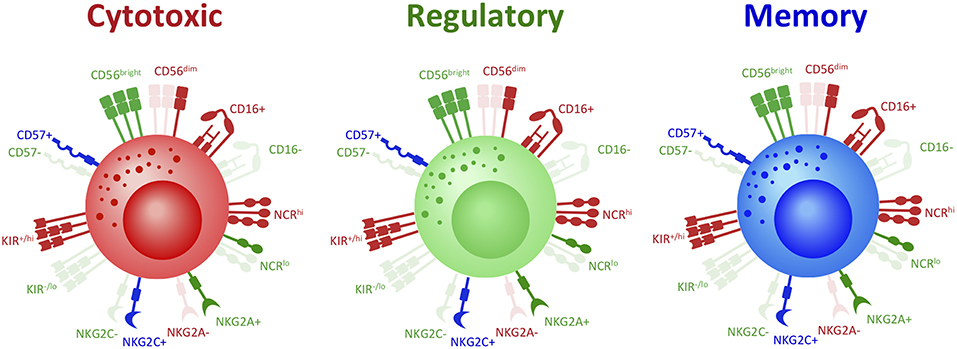
CD57 expression during T and NK cells differentiation. Proposed model... | Download Scientific Diagram

CD57 (Natural Killer Cell Marker) Ab-1 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody, Epredia™ 500μL; 200μg/mL; Unlabeled; Purified with BSA and azide Produkte | Fisher Scientific

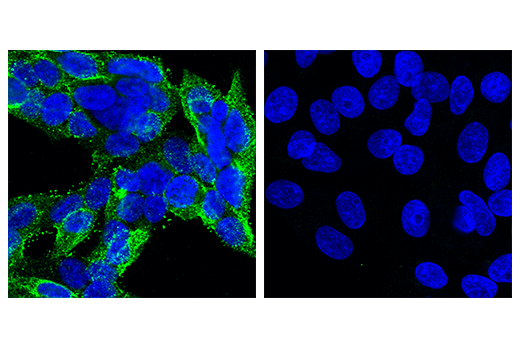
Senescence marker CD57 on T cells. ELA participants have more CD57 +... | Download Scientific Diagram
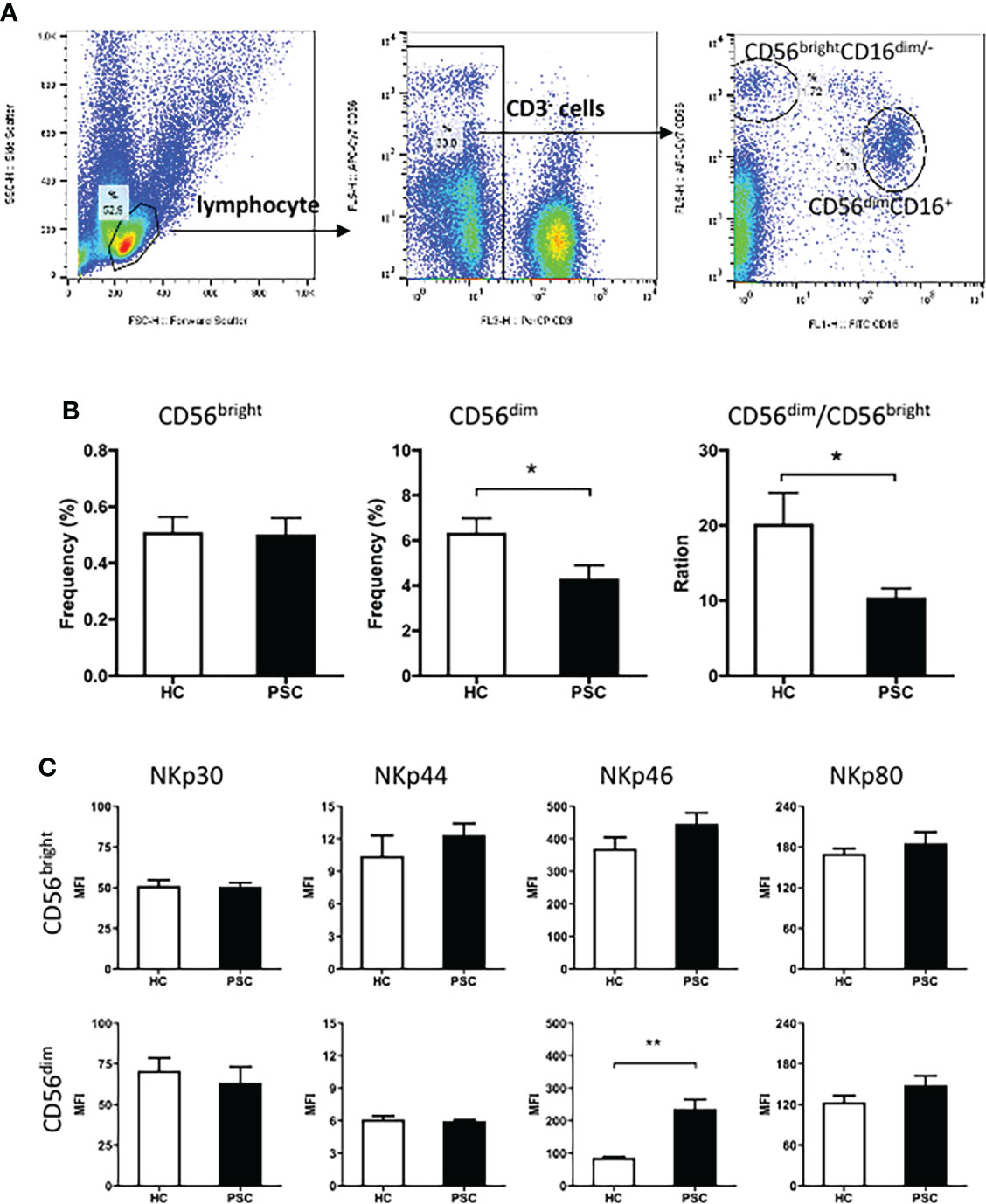
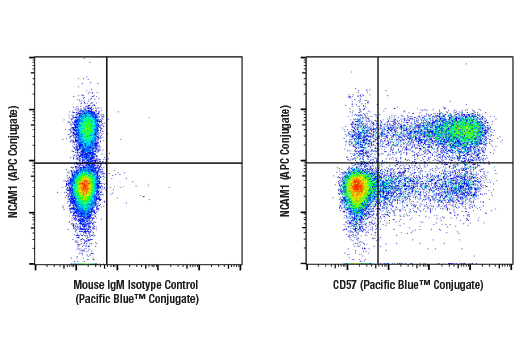
Frontiers | Decreased CD57 expression of natural killer cells enhanced cytotoxicity in patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis

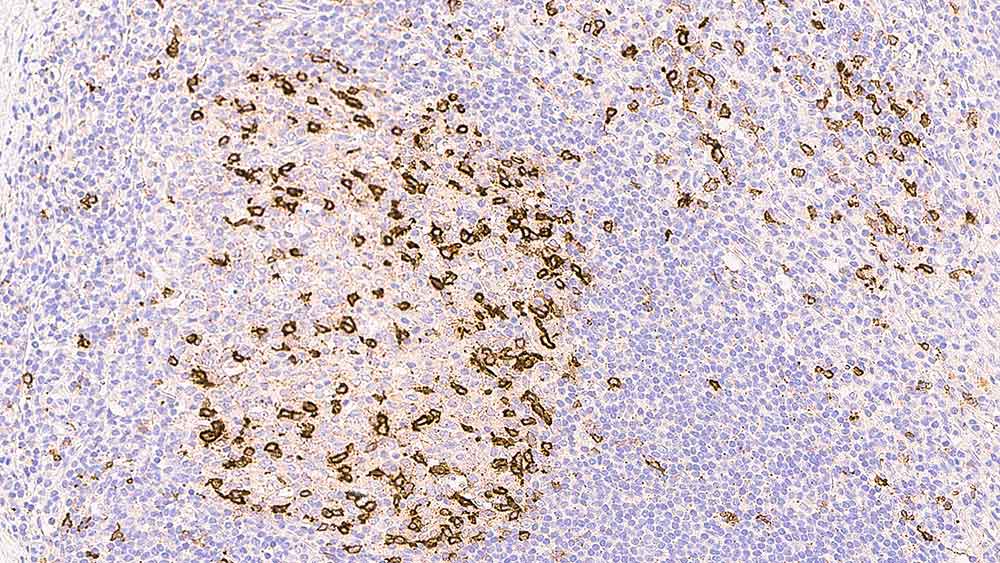
Prognostic significance of natural killer cell-associated markers in gastric cancer: quantitative analysis using multiplex immunohistochemistry | Journal of Translational Medicine | Full Text

Human CD57+ germinal center-T cells are the major helpers for GC-B cells and induce class switch recombination | BMC Immunology | Full Text
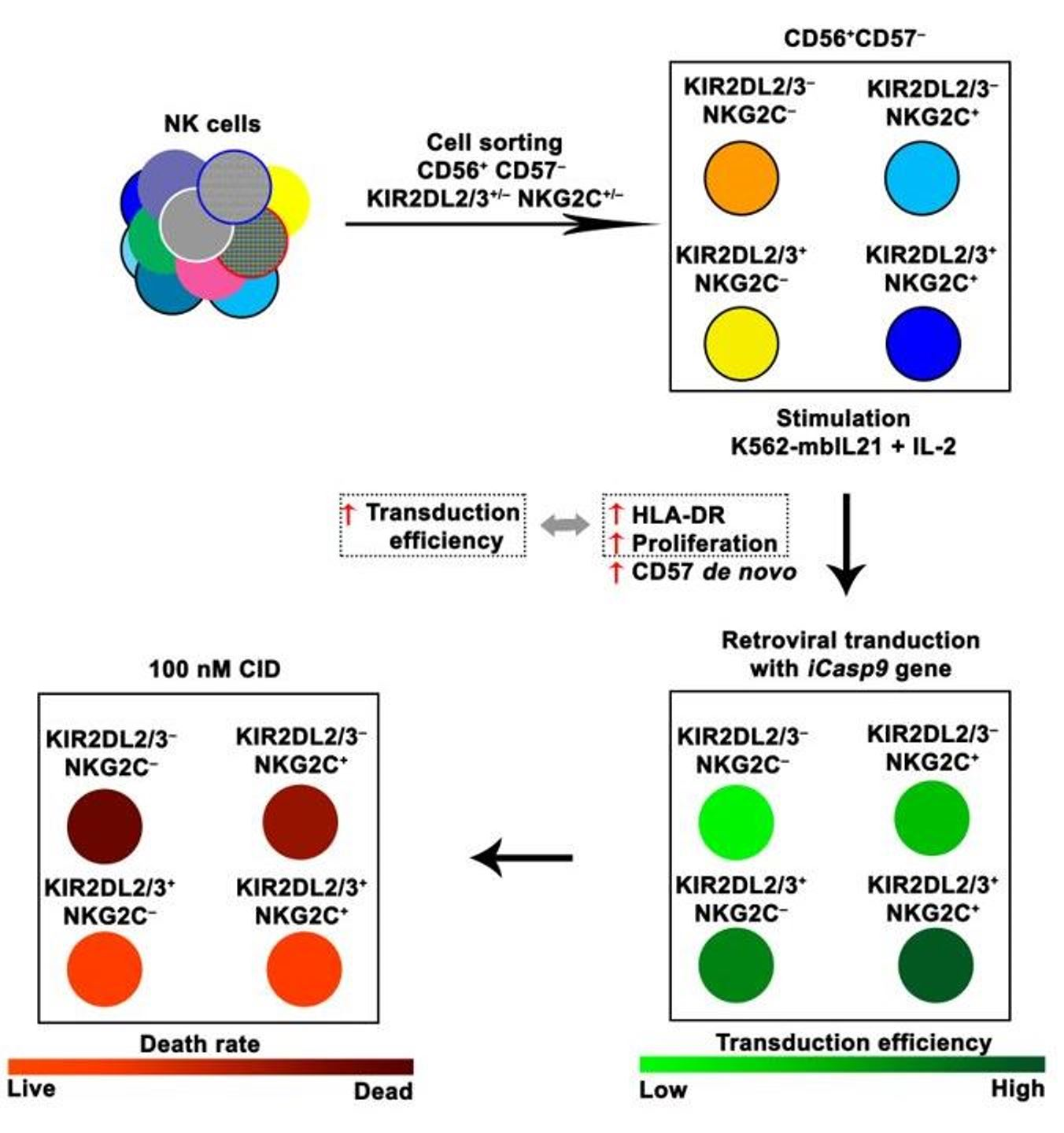
IJMS | Free Full-Text | Increased Susceptibility of the CD57− NK Cells Expressing KIR2DL2/3 and NKG2C to iCasp9 Gene Retroviral Transduction and the Relationships with Proliferative Potential, Activation Degree, and Death Induction

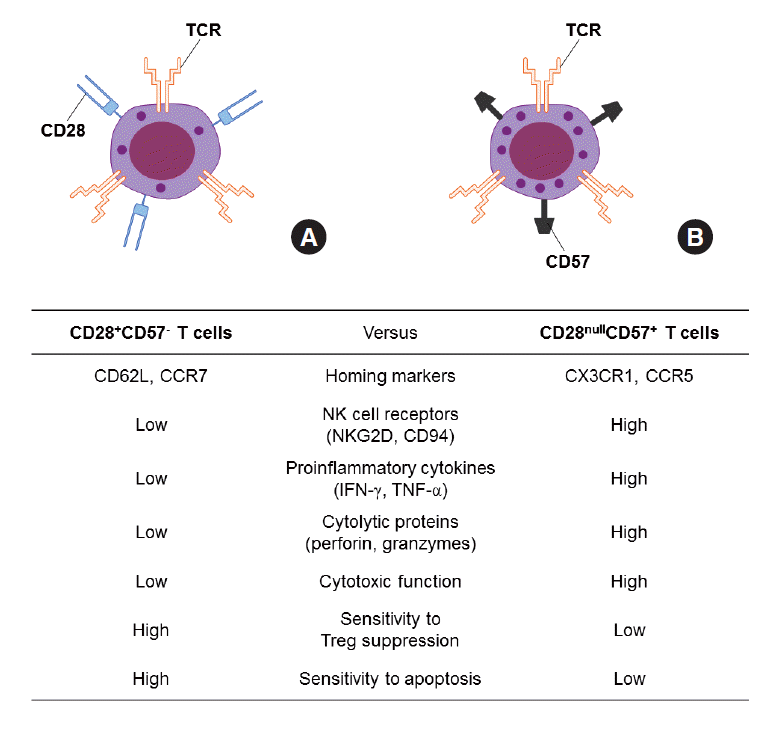
CD28 and CD57 define four populations with distinct phenotypic properties within human CD8+ T cells - Pangrazzi - 2020 - European Journal of Immunology - Wiley Online Library

Characterization of CD8+CD57+ T cells in patients with acute myocardial infarction | Cellular & Molecular Immunology

CD28 and CD57 define four populations with distinct phenotypic properties within human CD8+ T cells - Pangrazzi - 2020 - European Journal of Immunology - Wiley Online Library

Proteome Analysis of Distinct Developmental Stages of Human Natural Killer (NK) Cells - ScienceDirect
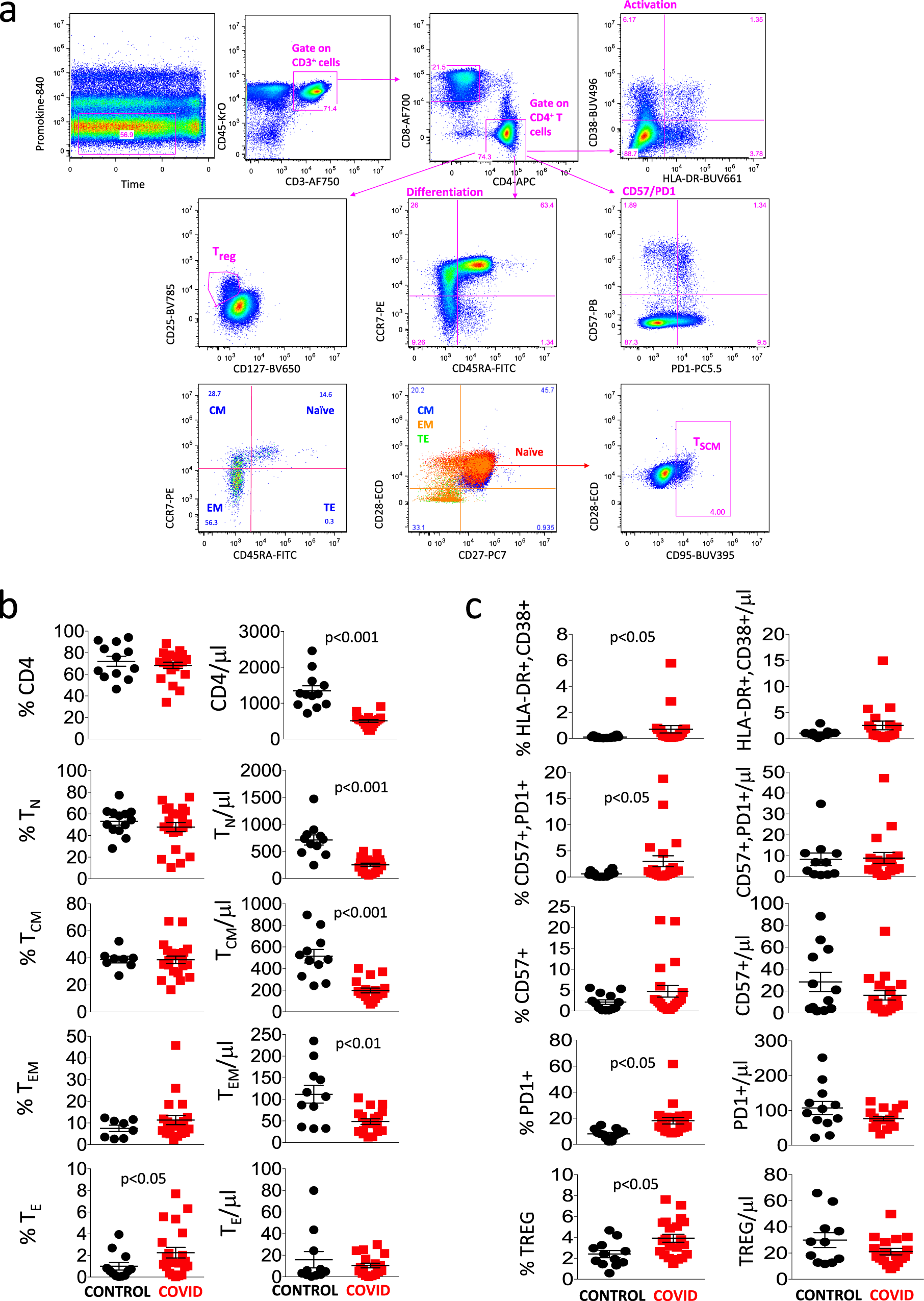
Marked T cell activation, senescence, exhaustion and skewing towards TH17 in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia | Nature Communications